
You have to play around with how it sits on the page, the layout of your poster.
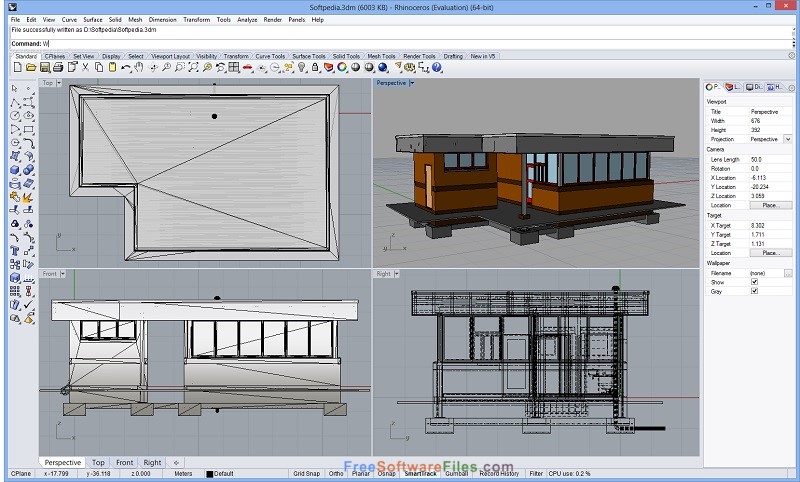
Taking a step back, we have to figure out how it’s going to sit on our poster, unless it is it going to be a single render used online. Where are the cameras placed? This would involve figuring out the dimensions of your render. The first step is to figure out your render views. Therefore, there’s no point modelling up everything to the smallest detail if it isn’t even being shown on your poster. You only need to resolve what’s shown on your sheet. Especially for a studio project like this, you don’t need to resolve the entire design. The way I worked this project (and this might change in the future), is that I started with a massing model from Sketchup.įrom that massing model, the very first thing I did was find out where I wanted the render view to be, where the camera is to be placed. The more detail you add to your virtual model, the better the render will look and the easier the post-editing process will be.
Rhinoceros 6 tutorial software#
On Rendering Quality level “Ultra” artificial lights will also cast normal based shadows.Rendering all starts in Rhino, Revit, Sketchup, or whatever software you’re modelling your design in. It’s active for sun light only when the Rendering Quality level is set to “High”. This feature further improves the depth perception of materials, especially with displacement maps. It is also worth noting that normal based self-shadowing of material surfaces implemented.
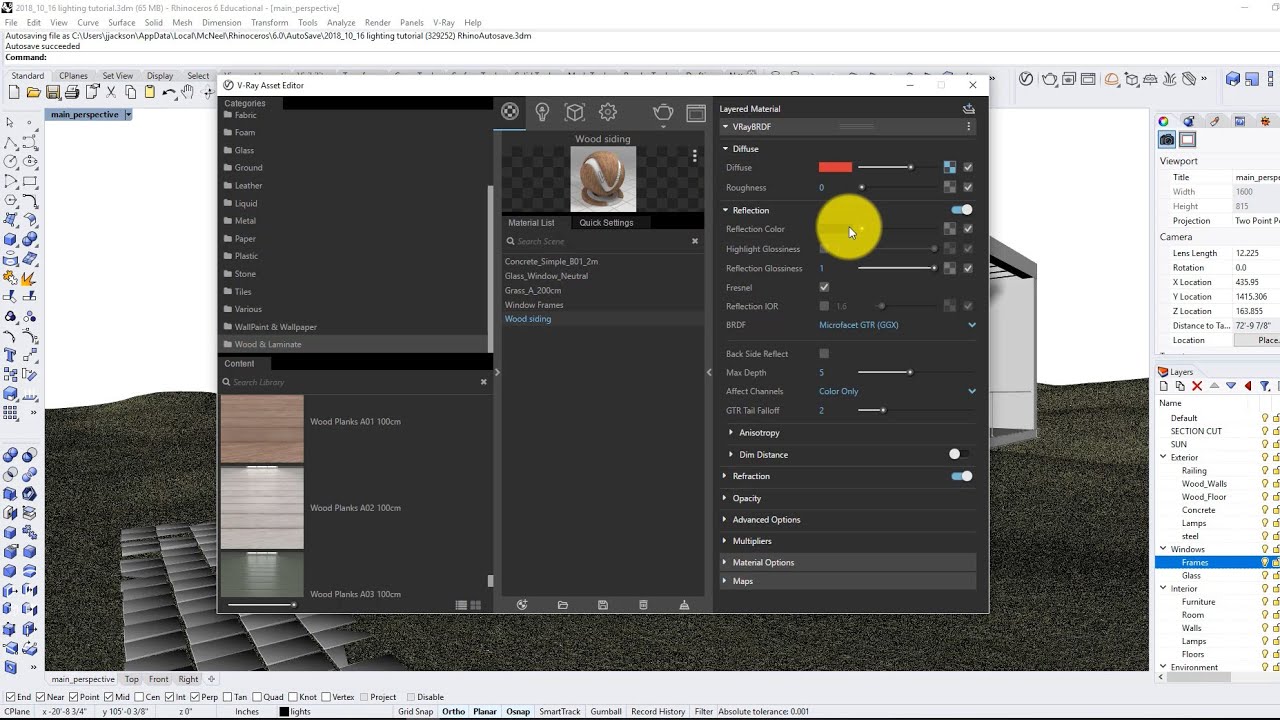
Textures that are available online, either paid for or free, will generally have a Normal, Bump / Height, Occlusion map included or available additionally to the basic Color texture.
Rhinoceros 6 tutorial full#
You can use this feature for noise on concrete surfaces, wood, tiling, or even full reliefs! This can go a long way in convincing the viewer that they are looking at a realistic picture.
Height maps can make for incredible surface detail and noise, without actually affecting or adding more geometry. Height maps are incredibly valuable for realism in your images and this can not be overstated enough! Furthermore, the brightness of Displacement maps cannot be further adjusted or inverted when editing the texture inside the Enscape Material Editor itself. It’s worth noting that Displacement maps are incompatible with transparent materials so the entire “Transparency” section becomes unavailable where a displacement map has been applied (including mask textures). The actual technique employed in Enscape is called quadtree parallax displacement mapping for optimum performance. Normally an Occlusion Map is the type of image you will use for Displacement maps. These RGB components correspond to the X, Y, and Z coordinates, respectively.ĭisplacement maps are an enhancement of the bump mapping or normal mapping techniques applied to textures. Normal map are a type of Bump map that require an image with RGB values. They tell Enscape to interpret a surface as protruding (bright parts of the texture) or recessed (dark parts of the texture). The Height option in the Enscape Material Editor allows you to utilize so called Bump, Normal, or Displacement maps in order to simulate bumps, wrinkles and dents and the lighting of these.īump maps can be any black and white 2D images. The amount by which it’s blurred is being determined by the Roughness value in the Reflections area. If the Frosted Glass checkbox is enabled, Enscape will blur what’s visible through the transparent surface.
Rhinoceros 6 tutorial free#
You know this effect from looking at a glass of water, or very thick glass.Īir has a refractive index of 1.0 – so light rays travel through it in a straight line -, water has an index of 1.33, window glass 1.52, and, for example diamonds have an index of 2.42 – they bend light quite heavily.įor further information on this topic, feel free to have a look at the Wikipedia article. The Refractive Index slider determines by which factor light is being bent when traveling through a transparent surface. This menu allows you to choose a color that should be added to any semi-transparent areas of your material. If you’re using it combined with a transparency map, it will define the maximum opacity, so white areas on said map will appear as opaque as you’ve set using this slider. The Opacity slider controls the overall transparency of the surface.

If you load a colored image, Enscape will automatically convert it to black and white, so you don’t have to worry about that. Grey areas will appear partially transparent, such as glass. It refers to the Opacity value, so a black area (which equals zero) on the image used will result in a close-to-perfectly transparent portion of the surface, while a white area will appear almost completely opaque. The Texture parameter allows you to control the transparency using a 2D image, a map.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
