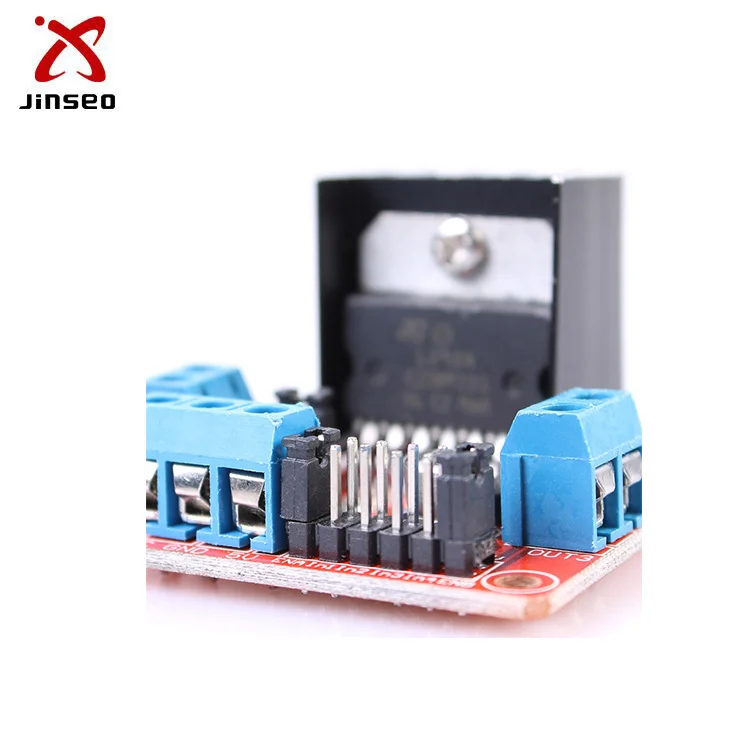


The L293D is designed to provide bidirectional drive currents of up to 600-mA at voltages from 4.5 V to 36 V. Hence, it is not wise to connect a DC motor directly to the microcontroller. Moreover, the voltage spikes produced while reversing the direction of rotation can easily damage the microcontroller. Most DC motors have power requirements well out of the reach of a microcontroller.
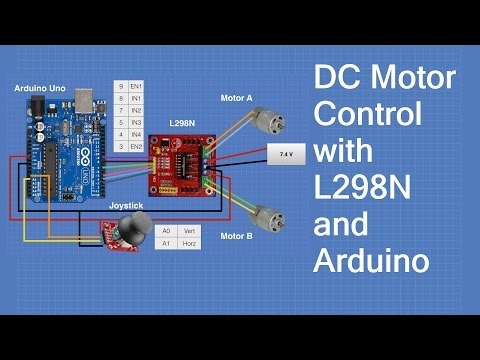
However, reversing the connections of these terminals will change the direction of rotation of the motor. How does a DC Motor work?Ī DC motor consists of two terminals, and some of the modules available in the market do not indicate the polarity. This stator and rotor move relative to each other for Electro-Mechanical Energy Conversion.Such a magnetic system with alternate N and S poles is called a heteropolar system. N and S poles are produced on both stator and rotor. This flux crosses the air gap from one core to the other. When windings are excited, a common flux is set up.Cores are laminated and made up of ferromagnetic materials to give optimum electric and magnetic characteristics. Both stator and rotor carry concentric cylindrical cores.The rotor is mounted on the shaft and bearings where the bearings are fixed to the stator frame.The clearance between the stator and rotor is called the air gap.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
